What is Ultimate Tensile Strength in Materials Testing?
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) refers to the maximum stress a material can endure while being stretched before it fails. It is a key measure in mechanical testing and is widely used to assess the strength and performance of metals, plastics, rubbers, composites, and other materials. In quality control and R&D, understanding what ultimate tensile strength is helps engineers choose materials suitable for load-bearing or structural applications.
Ultimate Tensile Strength Formula - How to Calculate UTS
The formula to calculate ultimate tensile strength is:
Where:
-
F = the maximum force applied (in newtons)
-
A = the original cross-sectional area of the specimen (in mm²)
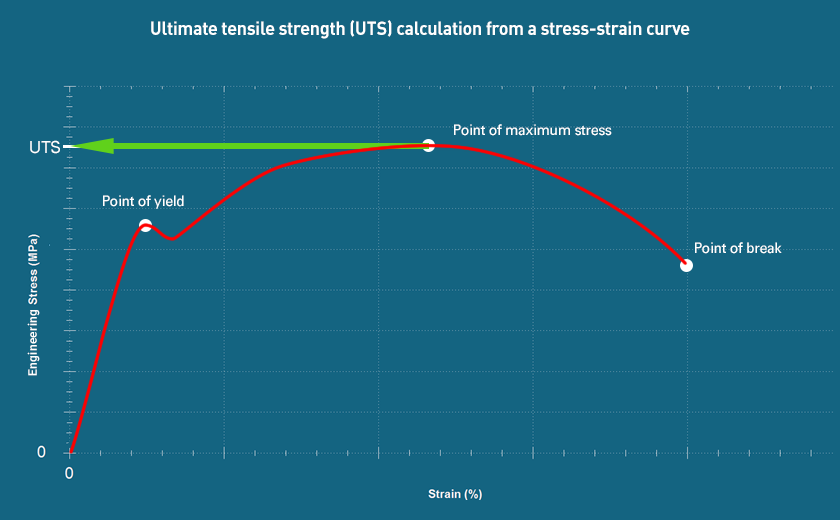
How to Calculate UTS
This gives a value in N/mm² or MPa. During a tensile test, the material is pulled until it breaks. The highest recorded force, divided by the original cross-sectional area, gives the UTS. This value is the peak on a stress-strain curve. Mecmesin tensile testers and extensometers are compatible with common industry standards, including ASTM D638, ISO 527, ASTM E8, and ISO 6892.
Advantages of High Ultimate Tensile Strength
To calculate ultimate tensile strength in practice, a specimen is mounted in a tensile testing machine and stretched at a constant rate until it breaks. The machine measures both force and elongation, recording data throughout the test. Software such as Mecmesin’s VectorPro calculates the UTS from the maximum force and initial cross-sectional area. Test parameters can be configured to meet international standards like ISO 37, ISO 6259, or ASTM D412, ensuring consistent and repeatable testing across material types.
When High Ultimate Tensile Strength is a Disadvantage
While high UTS materials are strong, they can also be brittle and less ductile. In applications that require flexibility or impact absorption - such as packaging, medical devices, or consumer products - these materials may fracture without warning. For these use cases, a balance between tensile strength and elongation is often required. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for effective material selection.
FAQs about Ultimate Tensile Strength
What is ultimate tensile strength?
Ultimate tensile strength (UTS) is the highest amount of tensile stress a material can resist before it breaks. It’s a key property used to evaluate material performance under tension.
How do you calculate ultimate tensile strength?
UTS is calculated using the formula: UTS = F / A, where F is the maximum applied force and A is the specimen’s original cross-sectional area. The result is expressed in megapascals (MPa) or newtons per square millimetre (N/mm²).
What is the formula for ultimate tensile strength?
The formula is UTS = F / A. This calculation provides the material’s maximum tensile stress based on the force applied and the specimen’s original cross-sectional area.
Which standards are used for tensile strength testing?
Common standards include ASTM D638, ISO 527 (plastics), ASTM E8 and ISO 6892 (metals), ISO 37 (rubber), and ASTM D412. Mecmesin testing equipment and software are fully compatible with these standards.
Standards
Featured or equivalent test standards for Mecmesin solutions in this section


